Center for Nanomaterials & MEMS
About
Research in nano materials and MEMS has recently gained momentum with many academicians, researchers and industries taking active part in it. The Centre has been carrying out collaborative work with all National MEMS Design Centre across the country with the help of Professors at CeNSE and ECE Departments of Indian Institute of Science (IISc). The area is a multidisciplinary field hence when students and faculty take active part in this research, they get a complete view of different facets of Science and Technology and its applications. This helps in building a connection between industry and academia. Centre for Nanomaterials and MEMS at NMIT, has been instituted to nurture the research abilities and innovative thinking capabilities among the students and faculty members. The objective is to give knowledge and create awareness on significant aspects of different technologies, highlighting the current trends and future directions in multidisciplinary areas like Electronics, Energy, chemical, Civil, Mechanical, Space, Medicine, Health care etc.
In the Centre for Nanomaterials and MEMS (CNM) at NMIT, we have dynamic multidisciplinary group of researchers oriented and working for the objectives, in the following research areas:
- Design, Simulation and Development of Micro-Electro-Mechanical systems (MEMS)
- Thin Film Materials Science and Engineering
- NanoMaterials Synthesis for biosensing application
Facility
- Scanning electron microscope (central facility)
- UV Visible Spectrometer
- Electrochemical Analyzer
- RF / DC Sputtering System
- E-Beam Evaporation System
- Resistive Thermal Evaporation System
- Tubular Chemical Vapor Deposition System
- Keithley 2450 source meter
- Probe sonicator
- Pelletizer
- Spin coater
- Magnetic Stirrer & Heater
- pH meter
- Muffle Furnace
Highlights
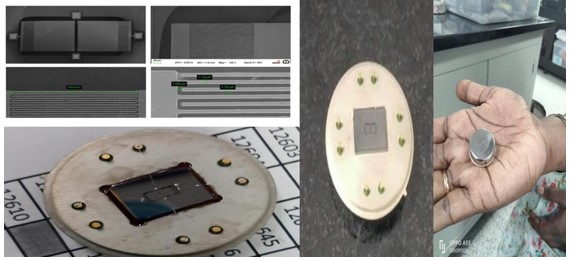
Design, Simulation, Fabrication, Packaging, and characterization of MEMS-based Sound Source localizer for Gunshot events.
A novel MEMS sound source localizer for gunshot events development was carried out at the Centre for Nanomaterials and MEMS, Nitte Meenakshi Institute of Technology, Bengaluru. The ARMAMENT Research Board, ARDE, DRDO Lab, Pune, awarded this project with a grant worth Rs. 25 lakhs. The project was implemented successfully and delivered on time to the funding agency. The principal investigators of the project were Ms. Nithya G., Department of ECE, NMIT, Bengaluru, and Dr. P N. Tengli, Department of Aero, NMIT, Bengaluru.
The design and modelling were executed exclusively at the Centre for Nanomaterials and MEMS, NMIT, Bengaluru. The device was fabricated and characterized successfully at CeNSE, Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru, with the support of Infab Technologies, and later packaged with the support of SITAR, DRDO, Bengaluru, and CMTI, Bengaluru.
This project aimed at developing a miniaturized sensor that can detect the direction of incoming sound signals from gunshots. This approach is aimed at mounting the directional acoustic sensor on the Indian soldier’s armament such that the soldier is aware of the direction of incoming gunshot events from the enemies and takes precautionary measures to overcome the gun violence and know the exact location of the enemy. The novel Biomimetic Microphone has two membranes that are mechanically coupled to achieve directionality in the sensing layer.